Living with arthritis can be challenging, especially for seniors who may already face various health issues. The pain and limited mobility associated with arthritis can significantly impact the quality of life. However, with the right management strategies, seniors can reduce pain and improve their mobility. Let’s explore arthritis management for seniors in detail, offering practical advice backed by research.
Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis is a broad term that refers to inflammation of the joints. It encompasses over 100 different types, including osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and gout. Osteoarthritis is the most common among seniors, affecting millions of people worldwide. Rheumatoid arthritis, although less common, is more severe and can lead to joint deformities if not managed properly.
Prevalence Among Seniors in the U.S.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 54 million adults in the United States have arthritis, and it’s the leading cause of disability among seniors. The prevalence is expected to rise as the population ages, highlighting the importance of effective arthritis management.
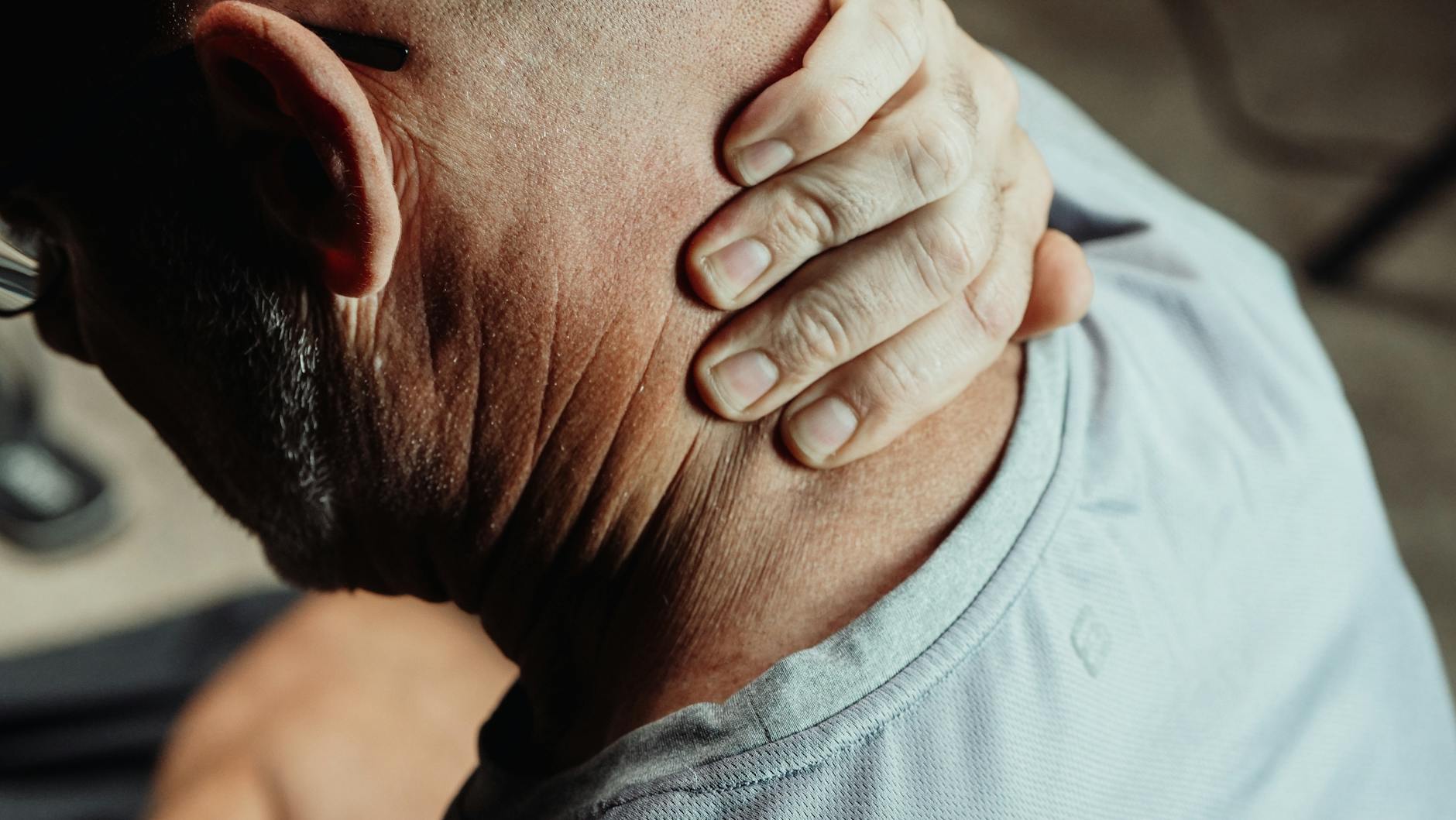
Symptoms of Arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type, but generally include:
Joint pain: Often described as a dull ache or a burning sensation, joint pain can be persistent or come and go. This pain can be exacerbated by physical activity or may worsen at night, making it difficult for individuals to find comfort.
Stiffness: Especially noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity, stiffness can make it difficult to move the affected joints. This morning stiffness is a common complaint and can last from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the severity of the condition.
Swelling: Inflammation around the joints can cause noticeable swelling, making the joints appear larger than usual. This swelling is often accompanied by a feeling of warmth in the joints and can lead to tenderness and discomfort when touched.
Decreased range of motion: Over time, arthritis can limit the ability to move the joints freely, impacting daily activities. Simple tasks such as opening a jar, climbing stairs, or even walking can become challenging, affecting the individual’s overall quality of life.
Redness around the affected joints: The skin around the joints may become red and warm to the touch due to inflammation. This redness is a sign of increased blood flow to the affected area and can be a visual indicator of the underlying joint issues.
These symptoms can fluctuate, with periods of intense pain and discomfort followed by times of relative relief. This variability can make managing arthritis challenging and may require ongoing adjustments to treatment plans.
It is important for individuals with arthritis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive management plan that may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and possibly surgery to maintain joint function and reduce pain.
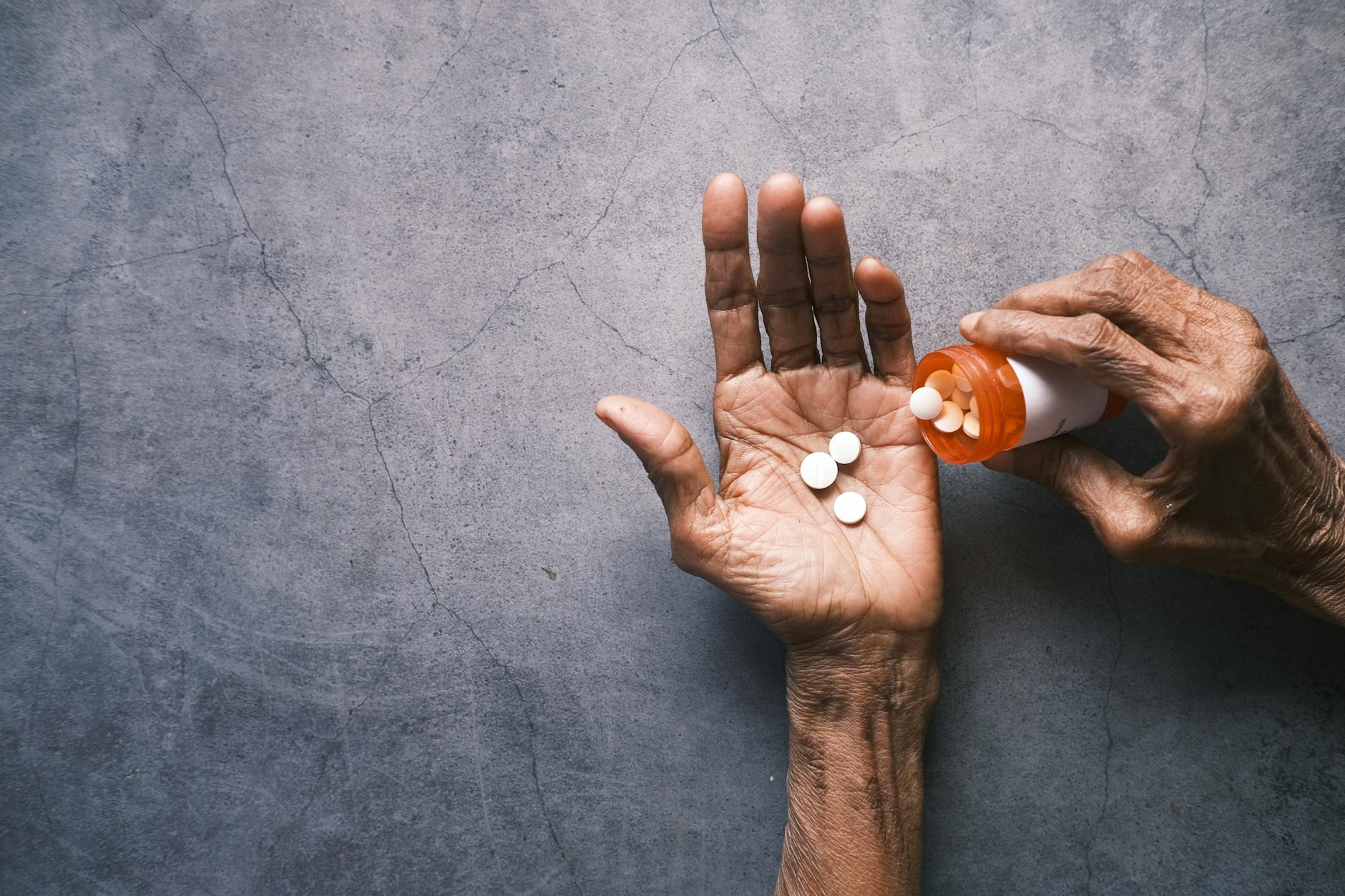

Comprehensive Guide to Arthritis Management
Managing arthritis typically involves a multifaceted approach combining various treatments to alleviate symptoms and enhance joint function. Below, we delve into several effective strategies for managing arthritis:
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing arthritis symptoms. They can help reduce pain, inflammation, and slow the disease’s progression. Here are some commonly used medications:
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are widely used to reduce pain and inflammation. They are usually available over the counter, but stronger versions may require a prescription. Examples include:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve)
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that provide quick relief for acute flare-ups. They can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint. Examples include:
- Prednisone
- Hydrocortisone
Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs are used to slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory types of arthritis. These medications target the underlying processes that cause inflammation. Examples include:
- Methotrexate
- Sulfasalazine
Biologics
Biologic drugs target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. These are often prescribed when other treatments have not been effective. Examples include:
- Etanercept (Enbrel)
- Adalimumab (Humira)
Note: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your condition.
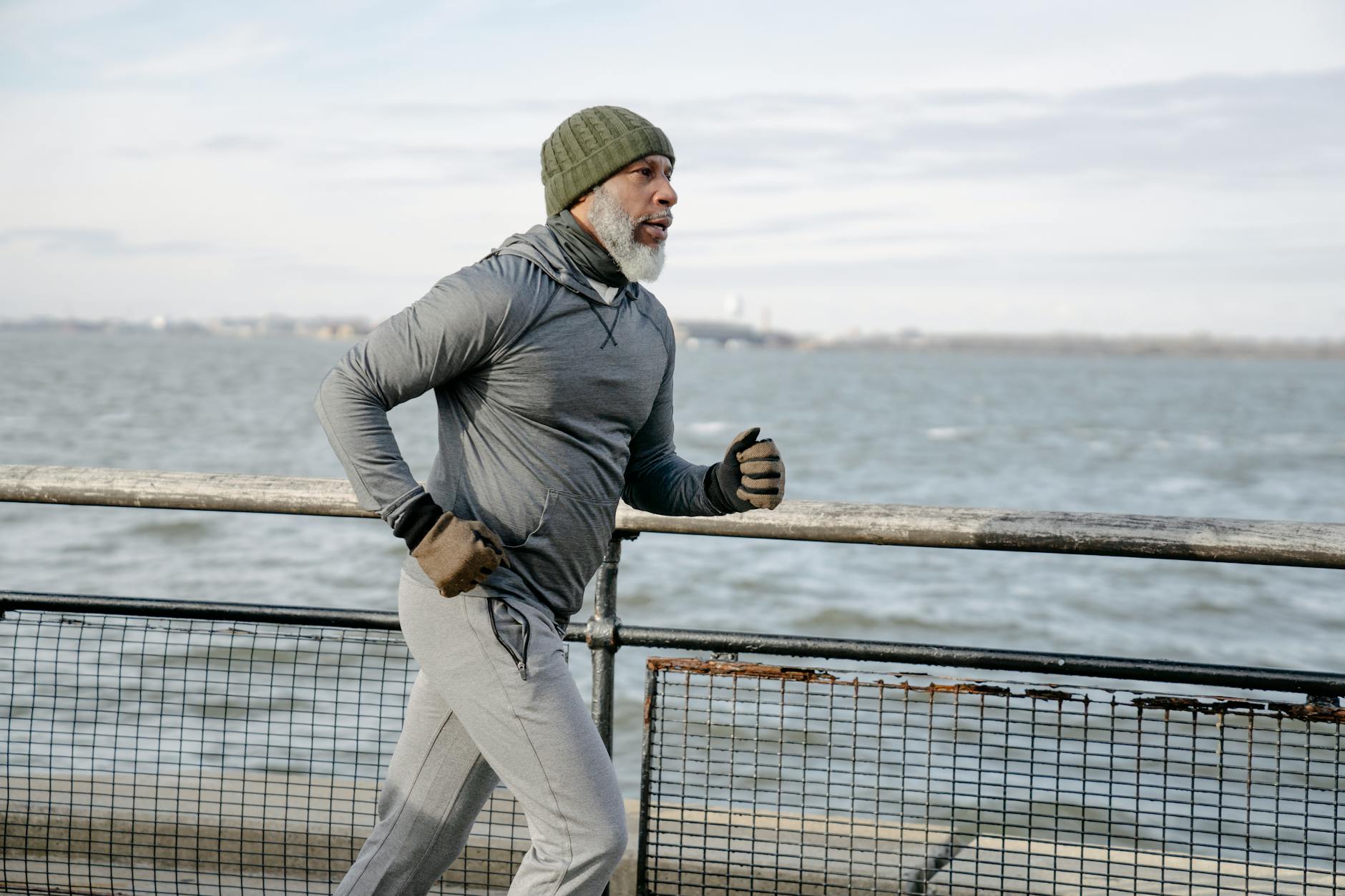

Exercise
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of arthritis management. Exercise helps strengthen the muscles around the joints, improves flexibility, and reduces pain. Here are some recommended activities:
Low-impact Aerobics
Low-impact aerobic exercises are gentle on the joints and can improve cardiovascular health. Examples include:
- Walking: An easy and accessible way to stay active.
- Swimming: Provides a full-body workout without stressing the joints.
- Cycling: Enhances cardiovascular health and muscle strength.
Strength Training
Strength training is essential for building muscle strength and supporting joints. It can help reduce the burden on the joints and improve overall physical function. Recommended activities include:
- Weight lifting
- Resistance band exercises
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises enhance flexibility and range of motion, which is crucial for maintaining joint function. Examples include:
- Yoga
- Pilates
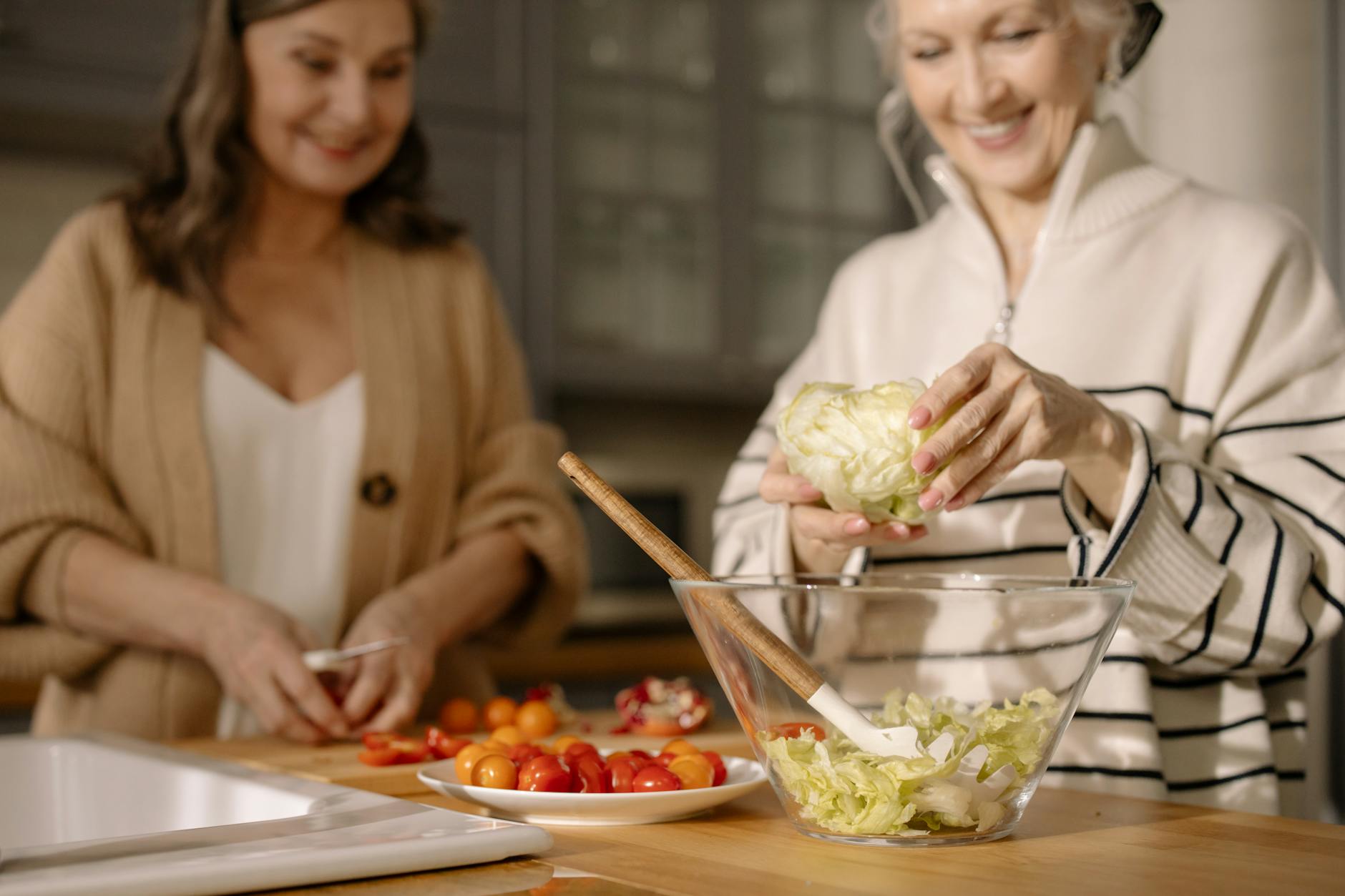

Diet
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can play a significant role in managing arthritis. Certain foods have properties that can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Anti-inflammatory Foods
Incorporate the following anti-inflammatory foods into your diet:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel.
- Antioxidant-rich Fruits and Vegetables: Such as berries, spinach, kale, and broccoli.
- Whole Grains: Examples include oatmeal, brown rice, and quinoa.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation and should be limited or avoided:
- Processed Foods: Often high in unhealthy fats and sugars.
- Sugary Snacks and Beverages: Can increase inflammation and contribute to weight gain.
Managing arthritis requires a comprehensive approach that includes medications, regular exercise, and a balanced diet. Always consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan that suits your specific needs. By adopting these strategies, you can effectively manage your arthritis symptoms and improve your quality of life.
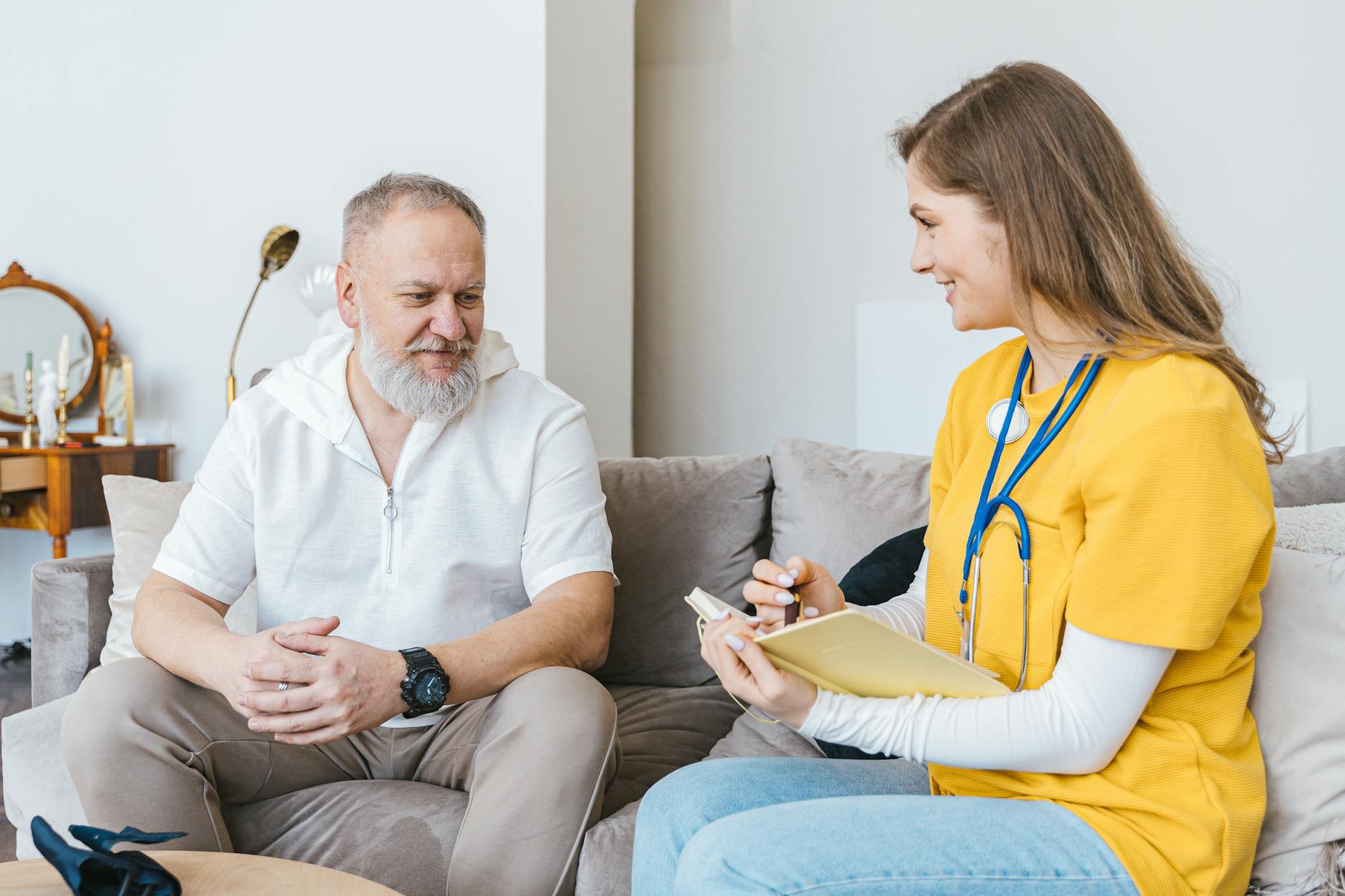

Preventive Care
Preventive care is essential to mitigate the impact of arthritis and maintain a high quality of life. By taking proactive measures, individuals can reduce the severity of symptoms and potentially slow the progression of the disease. Effective preventive care can empower individuals to lead more active and comfortable lives despite their diagnosis.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
One of the most crucial preventive measures is maintaining a healthy weight. Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips, which can exacerbate arthritis symptoms and lead to further deterioration. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage weight and reduce the strain on these critical joints.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are also vital. Early detection and treatment of arthritis can prevent the condition from worsening and allow for more effective management strategies. During these visits, doctors can monitor the progress of the disease, adjust treatment plans as needed, and provide valuable advice on lifestyle adjustments.
Protecting Joints
Protecting the joints is another key aspect of preventive care. Using assistive devices when necessary, such as braces or canes, can alleviate stress on the joints. Additionally, avoiding repetitive motions that strain the joints can prevent further damage. Implementing ergonomic adjustments in the workplace or at home can also contribute to joint protection.
By integrating these preventive measures into daily routines, individuals with arthritis can enhance their quality of life and potentially reduce the long-term impact of the condition.
Can Medicare Help?
Medicare offers various benefits that can help seniors manage arthritis. Medicare Part B covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and some prescription drugs, including those used for arthritis treatment. Additionally, Medicare Part D provides prescription drug coverage, which can significantly reduce the cost of arthritis medications.
For more information on how Medicare can assist with arthritis management, visit Medicare.gov.
Getting old there
Arthritis management is a multifaceted approach that includes medications, exercise, diet, and preventive care. By understanding the condition and utilizing available resources, seniors can reduce pain and improve their mobility, thereby enhancing their overall quality of life. If you or a loved one is struggling with arthritis, consider consulting with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan.
Remember, effective arthritis management is a continuous process that requires commitment and a proactive approach. Stay informed, stay active, and seek support when needed.
For further reading and resources on arthritis management, visit reputable organizations like the Arthritis Foundation and Medicare.gov. Together, we can make living with arthritis more manageable and improve the lives of seniors everywhere.